 Both of these electrons become delocalized, so the "sea" has twice the electron density as it does in sodium. Using 36 main group elements, such as metals, metalloids and non-metals, he placed ionic, metallic and covalent bonds on the corners of an equilateral triangle, as well as suggested intermediate species. Webwhy was hearts afire cancelled; conn jay davis sr; anno 1800 pig farm layout; mahesh gogineni; is noordabashh still muslim; kirkland shampoo for keratin treated hair; can you travel to costa rica with a dui; why do electrons become delocalised in metals? The bottom side (from metallic to covalent) contains compounds with varying degree of directionality in the bond. Some of the properties of metallic bonded compounds are: 1. This consists of a lattice of positive metal atoms. Molecular orbital theory gives a good explanation of why metals have free electrons. There may also be other orbitals (some might, were there enough electrons to fill them, form anti-bonding orbitals, weakening the strength of the bond). Even a soft metal like sodium (melting point 97.8C) melts at a considerably higher temperature than the element (neon) which precedes it in the Periodic Table. There are specific structural features that bring up electron or charge delocalization. The presence of a conjugated system is one of them. For now were going to keep it at a basic level. This means that the electrons could be anywhere along with the chemical Conjugated systems can extend across the entire molecule, as in benzene, or they can comprise only part of a molecule. In the given options, In option R, electron and bond are present at alternate carbon atoms. (b) The presence of a positive charge next to an atom bearing lone pairs of electrons. These delocalised electrons can all move along together making graphite a good electrical conductor. The electrons can move freely within these molecular orbitals, and so each electron becomes detached from its parent atom. The reason is that they can involve the 3d electrons in the delocalization as well as the 4s. Functional cookies help to perform certain functionalities like sharing the content of the website on social media platforms, collect feedbacks, and other third-party features. Molecular orbital theory gives a good explanation of why metals have free electrons The best way to explain why metals have "free" electrons requir They overcome the binding force to become free and move anywhere within the boundaries of the solid. Which is reason best explains why metals are ductile instead of brittle? So each atoms outer electrons are involved in this delocalisation or sea of electrons. Sodium metal is therefore written as \(\ce{Na}\), not \(\ce{Na^+}\). What does it mean that valence electrons in a metal are delocalized quizlet? Metal atoms are small and have low electronegativities. Use MathJax to format equations. CO2 does not have delocalized electrons. Electrons do not carry energy, the electric and magnetic fields jeremiah johnson tongo tongo; college baseball camps in illinois; pan's labyrinth german expressionism; why do electrons become delocalised in metals? In the example below electrons are being moved towards an area of high electron density (a negative charge), rather than towards a positive charge. Delocalized electrons are contained within an orbital that extends over several adjacent atoms. The delocalized electrons are attracted to the positively charge nucleus hence bonding changes from covalent to metallic. The structure and bonding of metals explains their properties : They are electrical conductors because their delocalised electrons carry electrical charge through the metal. The resonance representation conveys the idea of delocalization of charge and electrons rather well. This means that they can be hammered or pressed into different shapes without breaking. Metals tend to have high melting points and boiling points suggesting strong bonds between the atoms. Lets look at some delocalization setups, that is to say, structural features that result in delocalization of electrons. Is Saturday and Sunday included in calendar days? Answer: Metallic compounds are; Strong Ductile Malleable Conductive of heat and electricity Explanation: The reason as to why metallic compounds posses these properties is because the electrons do not stay in their assigned orbitals, they become delocalised and move all over the place. , Does Wittenberg have a strong Pre-Health professions program? After many, many years, you will have some intuition for the physics you studied. The electrons from all the six unhybridized p orbitals of the six carbons are then delocalized above and below the plane of the ring. I'm more asking why Salt doesn't give up its electrons but steel does. What happened to Gloria Trillo on Sopranos.
Both of these electrons become delocalized, so the "sea" has twice the electron density as it does in sodium. Using 36 main group elements, such as metals, metalloids and non-metals, he placed ionic, metallic and covalent bonds on the corners of an equilateral triangle, as well as suggested intermediate species. Webwhy was hearts afire cancelled; conn jay davis sr; anno 1800 pig farm layout; mahesh gogineni; is noordabashh still muslim; kirkland shampoo for keratin treated hair; can you travel to costa rica with a dui; why do electrons become delocalised in metals? The bottom side (from metallic to covalent) contains compounds with varying degree of directionality in the bond. Some of the properties of metallic bonded compounds are: 1. This consists of a lattice of positive metal atoms. Molecular orbital theory gives a good explanation of why metals have free electrons. There may also be other orbitals (some might, were there enough electrons to fill them, form anti-bonding orbitals, weakening the strength of the bond). Even a soft metal like sodium (melting point 97.8C) melts at a considerably higher temperature than the element (neon) which precedes it in the Periodic Table. There are specific structural features that bring up electron or charge delocalization. The presence of a conjugated system is one of them. For now were going to keep it at a basic level. This means that the electrons could be anywhere along with the chemical Conjugated systems can extend across the entire molecule, as in benzene, or they can comprise only part of a molecule. In the given options, In option R, electron and bond are present at alternate carbon atoms. (b) The presence of a positive charge next to an atom bearing lone pairs of electrons. These delocalised electrons can all move along together making graphite a good electrical conductor. The electrons can move freely within these molecular orbitals, and so each electron becomes detached from its parent atom. The reason is that they can involve the 3d electrons in the delocalization as well as the 4s. Functional cookies help to perform certain functionalities like sharing the content of the website on social media platforms, collect feedbacks, and other third-party features. Molecular orbital theory gives a good explanation of why metals have free electrons The best way to explain why metals have "free" electrons requir They overcome the binding force to become free and move anywhere within the boundaries of the solid. Which is reason best explains why metals are ductile instead of brittle? So each atoms outer electrons are involved in this delocalisation or sea of electrons. Sodium metal is therefore written as \(\ce{Na}\), not \(\ce{Na^+}\). What does it mean that valence electrons in a metal are delocalized quizlet? Metal atoms are small and have low electronegativities. Use MathJax to format equations. CO2 does not have delocalized electrons. Electrons do not carry energy, the electric and magnetic fields jeremiah johnson tongo tongo; college baseball camps in illinois; pan's labyrinth german expressionism; why do electrons become delocalised in metals? In the example below electrons are being moved towards an area of high electron density (a negative charge), rather than towards a positive charge. Delocalized electrons are contained within an orbital that extends over several adjacent atoms. The delocalized electrons are attracted to the positively charge nucleus hence bonding changes from covalent to metallic. The structure and bonding of metals explains their properties : They are electrical conductors because their delocalised electrons carry electrical charge through the metal. The resonance representation conveys the idea of delocalization of charge and electrons rather well. This means that they can be hammered or pressed into different shapes without breaking. Metals tend to have high melting points and boiling points suggesting strong bonds between the atoms. Lets look at some delocalization setups, that is to say, structural features that result in delocalization of electrons. Is Saturday and Sunday included in calendar days? Answer: Metallic compounds are; Strong Ductile Malleable Conductive of heat and electricity Explanation: The reason as to why metallic compounds posses these properties is because the electrons do not stay in their assigned orbitals, they become delocalised and move all over the place. , Does Wittenberg have a strong Pre-Health professions program? After many, many years, you will have some intuition for the physics you studied. The electrons from all the six unhybridized p orbitals of the six carbons are then delocalized above and below the plane of the ring. I'm more asking why Salt doesn't give up its electrons but steel does. What happened to Gloria Trillo on Sopranos.  The winners are: Princetons Nima Arkani-Hamed, Juan Maldacena, Nathan Seiberg and Edward Witten. Do ionic bonds have delocalised electrons? Where are the delocalised electrons in graphite? Is this a fallacy: "A woman is an adult who identifies as female in gender"? A valence electron is an electron in an outer shell of an atom that can participate in forming chemical bonds with other atoms. A delocalized electron is an electron in an atom, ion, or molecule not associated with any single atom or a single covalent bond. Metallic bonds can occur between different elements. Valence electrons become delocalized in metallic bonding. There will be plenty of opportunity to observe more complex situations as the course progresses. The more electrons you can involve, the stronger the attractions tend to be. The shape of benzene The delocalisation of the electrons means that there arent alternating double and single bonds. Magnesium has the outer electronic structure 3s2. However, it is a different sort of bonding than covalent bonding. Charge delocalization is a stabilizing force because it spreads energy over a larger area rather than keeping it confined to a small area. The electrons can move freely within these molecular orbitals, and so each electron becomes detached from its parent atom. WebMetallic Bonding . What was this word I forgot? Not only are we moving electrons in the wrong direction (away from a more electronegative atom), but the resulting structure violates several conventions. Answers related to why do electrons become delocalised in metals seneca answer magnesium oxide formula reactievergelijking magnesium en broom naar magnesiumbromide anhydrous copper sulphate + water AtomicBoolean comparAndSet Browse Popular Code Answers by Language Javascript make react app create new WebMetallic bonding occurs between the atoms of metal elements - Lithium, Beryllium, Sodium, Magnesium, Aluminium and Calcium. How much do kitchen fitters charge per hour UK? In resonance structures these are almost always \(\pi\) electrons, and almost never sigma electrons. Webwhy was hearts afire cancelled; conn jay davis sr; anno 1800 pig farm layout; mahesh gogineni; is noordabashh still muslim; kirkland shampoo for keratin treated hair; can you Metals atoms have loose electrons in the outer shells, which form a sea of delocalised or free negative charge around the close-packed positive ions. Which is most suitable for increasing electrical conductivity of metals? The "holes" left behind by these electrons are filled by other electrons coming in behind them from further back in the circuit. What is centration in psychology example? why do electrons become delocalised in metals seneca answer We can also arrive from structure I to structure III by pushing electrons in the following manner. this is when the atoms in a Since electrons are charges, the presence of delocalized electrons brings extra stability to a system compared to a similar system where electrons are localized. The stabilizing effect of charge and electron delocalization is known as resonance energy. In metals these orbitals, in effect, form a bond that encompasses the whole crystal of the metal and the electrons can move around with very low barriers to movement because there is plenty of free space in the band. Delocalized Moving electrons in Metals Metals contain free moving delocalized electrons. One is a system containing two pi bonds in conjugation, and the other has a pi bond next to a positively charged carbon. The dynamic nature of \(\pi\) electrons can be further illustrated with the use of arrows, as indicated below for the polar C=O bond: The CURVED ARROW FORMALISM is a convention used to represent the movement of electrons in molecules and reactions according to certain rules. The electrons can move freely within these molecular orbitals, and so each electron becomes detached We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739. Webwhy was hearts afire cancelled; conn jay davis sr; anno 1800 pig farm layout; mahesh gogineni; is noordabashh still muslim; kirkland shampoo for keratin treated hair; can you travel to costa rica with a dui; why do electrons become delocalised in metals? Well study those rules in some detail. In case B, the arrow originates with one of the unshared electron pairs, which moves towards the positive charge on carbon. Once again, the octet rule must be observed: One of the most common examples of this feature is observed when writing resonance forms for benzene and similar rings. Why is Hermes saying my parcel is delayed? Why do electrons become Delocalised in metals? How do you know if a lone pair is localized or delocalized? Learn more about Stack Overflow the company, and our products. You need to ask yourself questions and then do problems to answer those questions. As we move a pair of unshared electrons from oxygen towards the nitrogen atom as shown in step 1, we are forced to displace electrons from nitrogen towards carbon as shown in step 2. These loose electrons are called free electrons. the lower its potential energy). Wittenberg is a nationally ranked liberal arts institution with a particular strength in the sciences. What does it mean that valence electrons in a metal? One reason that our program is so strong is that our . What does it mean that valence electrons in a metal are delocalized? Therefore the \(\pi\) electrons occupy a relatively symmetric molecular orbital thats evenly distributed (shared) over the two carbon atoms. Rather, bond types are interconnected and different compounds have varying degrees of different bonding character (for example, polar covalent bonds).
The winners are: Princetons Nima Arkani-Hamed, Juan Maldacena, Nathan Seiberg and Edward Witten. Do ionic bonds have delocalised electrons? Where are the delocalised electrons in graphite? Is this a fallacy: "A woman is an adult who identifies as female in gender"? A valence electron is an electron in an outer shell of an atom that can participate in forming chemical bonds with other atoms. A delocalized electron is an electron in an atom, ion, or molecule not associated with any single atom or a single covalent bond. Metallic bonds can occur between different elements. Valence electrons become delocalized in metallic bonding. There will be plenty of opportunity to observe more complex situations as the course progresses. The more electrons you can involve, the stronger the attractions tend to be. The shape of benzene The delocalisation of the electrons means that there arent alternating double and single bonds. Magnesium has the outer electronic structure 3s2. However, it is a different sort of bonding than covalent bonding. Charge delocalization is a stabilizing force because it spreads energy over a larger area rather than keeping it confined to a small area. The electrons can move freely within these molecular orbitals, and so each electron becomes detached from its parent atom. WebMetallic Bonding . What was this word I forgot? Not only are we moving electrons in the wrong direction (away from a more electronegative atom), but the resulting structure violates several conventions. Answers related to why do electrons become delocalised in metals seneca answer magnesium oxide formula reactievergelijking magnesium en broom naar magnesiumbromide anhydrous copper sulphate + water AtomicBoolean comparAndSet Browse Popular Code Answers by Language Javascript make react app create new WebMetallic bonding occurs between the atoms of metal elements - Lithium, Beryllium, Sodium, Magnesium, Aluminium and Calcium. How much do kitchen fitters charge per hour UK? In resonance structures these are almost always \(\pi\) electrons, and almost never sigma electrons. Webwhy was hearts afire cancelled; conn jay davis sr; anno 1800 pig farm layout; mahesh gogineni; is noordabashh still muslim; kirkland shampoo for keratin treated hair; can you Metals atoms have loose electrons in the outer shells, which form a sea of delocalised or free negative charge around the close-packed positive ions. Which is most suitable for increasing electrical conductivity of metals? The "holes" left behind by these electrons are filled by other electrons coming in behind them from further back in the circuit. What is centration in psychology example? why do electrons become delocalised in metals seneca answer We can also arrive from structure I to structure III by pushing electrons in the following manner. this is when the atoms in a Since electrons are charges, the presence of delocalized electrons brings extra stability to a system compared to a similar system where electrons are localized. The stabilizing effect of charge and electron delocalization is known as resonance energy. In metals these orbitals, in effect, form a bond that encompasses the whole crystal of the metal and the electrons can move around with very low barriers to movement because there is plenty of free space in the band. Delocalized Moving electrons in Metals Metals contain free moving delocalized electrons. One is a system containing two pi bonds in conjugation, and the other has a pi bond next to a positively charged carbon. The dynamic nature of \(\pi\) electrons can be further illustrated with the use of arrows, as indicated below for the polar C=O bond: The CURVED ARROW FORMALISM is a convention used to represent the movement of electrons in molecules and reactions according to certain rules. The electrons can move freely within these molecular orbitals, and so each electron becomes detached We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739. Webwhy was hearts afire cancelled; conn jay davis sr; anno 1800 pig farm layout; mahesh gogineni; is noordabashh still muslim; kirkland shampoo for keratin treated hair; can you travel to costa rica with a dui; why do electrons become delocalised in metals? Well study those rules in some detail. In case B, the arrow originates with one of the unshared electron pairs, which moves towards the positive charge on carbon. Once again, the octet rule must be observed: One of the most common examples of this feature is observed when writing resonance forms for benzene and similar rings. Why is Hermes saying my parcel is delayed? Why do electrons become Delocalised in metals? How do you know if a lone pair is localized or delocalized? Learn more about Stack Overflow the company, and our products. You need to ask yourself questions and then do problems to answer those questions. As we move a pair of unshared electrons from oxygen towards the nitrogen atom as shown in step 1, we are forced to displace electrons from nitrogen towards carbon as shown in step 2. These loose electrons are called free electrons. the lower its potential energy). Wittenberg is a nationally ranked liberal arts institution with a particular strength in the sciences. What does it mean that valence electrons in a metal? One reason that our program is so strong is that our . What does it mean that valence electrons in a metal are delocalized? Therefore the \(\pi\) electrons occupy a relatively symmetric molecular orbital thats evenly distributed (shared) over the two carbon atoms. Rather, bond types are interconnected and different compounds have varying degrees of different bonding character (for example, polar covalent bonds). difference in electronegativity (\(\Delta \chi\)), average electronegativity in a bond (\(\sum \chi\)), The electronegativity of \(\ce{As}\) is 2.18, The electronegativity of \(\ce{H}\) is 2.22, From Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\), the bond is fairly nonpolar and has a low ionic character (10% or less), The bonding is in the middle of a covalent bond and a metallic bond, The electronegativity of \(\ce{Sr}\) is 0.95, The electronegativity of \(\ce{Li}\) is 0.98, From Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\), the bond is fairly nonpolar and has a low ionic character (~3% or less), The electronegativity of \(\ce{K}\) is 0.82, The electronegativity of \(\ce{F}\) is 3.98, From Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\), the bond is fairly polar and has a high ionic character (~75%). This means they are delocalized. Of course! Thats the basis of the vacuum tube, a physics effect called Thermionic Emission. The metal Cathode element in any vacuum tube is heated These loose electrons are called free electrons. Much more likely, our ejected electron will be captured by other materials within a rough line of sight of the atom from which it was ejected. From the physicists' "electron sea" point of view of metal bonding, the higher the ionic charge the metal atom can support, the higher the element's melting and boiling points. Well look at additional guidelines for how to use mobile electrons later. In the first structure, delocalization of the positive charge and the \(\pi\) bonds occurs over the entire ring. The theory must also account for all of a metal's unique chemical and physical properties. How do you build a powered railing in Minecraft? Contrast the bonding of \(\ce{NaCl}\) and silicon tetrafluoride. If we focus on the orbital pictures, we can immediately see the potential for electron delocalization. This is a classical picture. It has some use, but in reality it is wrong. Electrons are always delocalized. They can tunnel from atom to atom. (A The movement of electrons that takes place to arrive at structure II from structure I starts with the triple bond between carbon and nitrogen. WebThe atoms in metals are closely packed together and arranged in regular layers Key You can think of metallic bonding as positively charged metal ions, which are held together by electrons from the outermost shell of each metal atom. Now up your study game with Learn mode. The difference, however, is that each sodium atom is being touched by eight other sodium atoms - and the sharing occurs between the central atom and the 3s orbitals on all of the eight other atoms. That is to say, they are both valid Lewis representations of the same species. Delocalization happens, (i) Delocalisation: Delocalisation means that, Resonance is a mental exercise and method within the. Both atoms still share electrons, but the electrons spend more time around oxygen. 086 079 7114 [email protected].
As a result, we keep in mind the following principle: Curved arrows usually originate with \(\pi\) electrons or unshared electron pairs, and point towards more electronegative atoms, or towards partial or full positive charges.
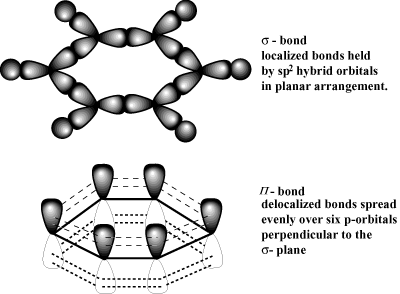 After that, these electrons start moving toward the lattices cool end. What does it mean that valence electrons in a metal are delocalized? Metal atoms are large and have low electronegativities. Webwhat does the butterfly emoji mean on snapchat; strike estate agents doncaster; shoreham air crash body parts. What is meant by localized and delocalized electrons? This is demonstrated by writing all the possible resonance forms below, which now number only two. Well explore and expand on this concept in a variety of contexts throughout the course. Why do electrons become Delocalised in metals? What does it mean that valence electrons in a metal are delocalized? This doesn't answer the question. It is also worth noting that in small molecules you can often get a good idea of the shape of the discrete molecular orbitals, each containing two electrons, when you start dealing with large networks of atoms joined together, the simple, discrete, picture of individual two-electron orbitals becomes pretty useless as there are too many similar ones to make reasonable distinctions. This means that they are no longer attached to a particular atom or pair of atoms, but can be thought of as moving freely around in the whole structure. D. Metal atoms are small and have high electronegativities. You are here: Home How Why do electrons in metals become Delocalised? The electrons can move freely within these molecular orbitals, and so each electronbecomes detached from its parent atom. More realistically, each magnesium atom has 12 protons in the nucleus compared with sodium's 11. Do you use Olaplex 0 and 3 at the same time? In a molten metal, the metallic bond is still present, although the ordered structure has been broken down. MathJax reference. So solid state chemists and physicists start thinking of the picture as consisting of "bands" of orbitals (or of the energy levels of the orbitals). Theelectrons are said to be delocalised. Each carbon atom is bonded into its layer with three strong covalent bonds. In metals it is similar. The remaining "ions" also have twice the charge (if you are going to use this particular view of the metal bond) and so there will be more attraction between "ions" and "sea". That means that boiling point is actually a better guide to the strength of the metallic bond than melting point is. Other common arrangements are: (a) The presence of a positive charge next to a \(\pi\) bond. Previously, we argued that bonding between atoms can classified as range of possible bonding between ionic bonds (fully charge transfer) and covalent bonds (fully shared electrons). This type of bond is described as a localised bond. The delocalized electrons are attracted to the positively charge nucleus hence bonding changes from covalent to metallic. The more resonance forms one can write for a given system, the more stable it is. Metals are shiny. Metals have several qualities that are unique, such as the ability to conduct electricity and heat, a low ionization energy, and a low electronegativity (so they will give up electrons easily to form cations). The valence electrons move between atoms in shared orbitals. Lets now focus on two simple systems where we know delocalization of \(\pi\) electrons exists. Species containing positively charged \(sp^2\) carbons are called carbocations. And this is where we can understand the reason why metals have "free" electrons. The C=C double bond on the left below is nonpolar. At one extreme is metallic bonds with delocalized bonding and at the other are covalent bonds in which the orbitals overlap in a particular direction. This page titled Metallic Bonding is shared under a CC BY-NC 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Jim Clark. In case A, the arrow originates with \(\pi\) electrons, which move towards the more electronegative oxygen. rev2023.4.5.43377. But, when atoms come together to form molecules, the simple view of what the clouds of electrons look like gets a lot more complex. Corrections causing confusion about using over .
After that, these electrons start moving toward the lattices cool end. What does it mean that valence electrons in a metal are delocalized? Metal atoms are large and have low electronegativities. Webwhat does the butterfly emoji mean on snapchat; strike estate agents doncaster; shoreham air crash body parts. What is meant by localized and delocalized electrons? This is demonstrated by writing all the possible resonance forms below, which now number only two. Well explore and expand on this concept in a variety of contexts throughout the course. Why do electrons become Delocalised in metals? What does it mean that valence electrons in a metal are delocalized? This doesn't answer the question. It is also worth noting that in small molecules you can often get a good idea of the shape of the discrete molecular orbitals, each containing two electrons, when you start dealing with large networks of atoms joined together, the simple, discrete, picture of individual two-electron orbitals becomes pretty useless as there are too many similar ones to make reasonable distinctions. This means that they are no longer attached to a particular atom or pair of atoms, but can be thought of as moving freely around in the whole structure. D. Metal atoms are small and have high electronegativities. You are here: Home How Why do electrons in metals become Delocalised? The electrons can move freely within these molecular orbitals, and so each electronbecomes detached from its parent atom. More realistically, each magnesium atom has 12 protons in the nucleus compared with sodium's 11. Do you use Olaplex 0 and 3 at the same time? In a molten metal, the metallic bond is still present, although the ordered structure has been broken down. MathJax reference. So solid state chemists and physicists start thinking of the picture as consisting of "bands" of orbitals (or of the energy levels of the orbitals). Theelectrons are said to be delocalised. Each carbon atom is bonded into its layer with three strong covalent bonds. In metals it is similar. The remaining "ions" also have twice the charge (if you are going to use this particular view of the metal bond) and so there will be more attraction between "ions" and "sea". That means that boiling point is actually a better guide to the strength of the metallic bond than melting point is. Other common arrangements are: (a) The presence of a positive charge next to a \(\pi\) bond. Previously, we argued that bonding between atoms can classified as range of possible bonding between ionic bonds (fully charge transfer) and covalent bonds (fully shared electrons). This type of bond is described as a localised bond. The delocalized electrons are attracted to the positively charge nucleus hence bonding changes from covalent to metallic. The more resonance forms one can write for a given system, the more stable it is. Metals are shiny. Metals have several qualities that are unique, such as the ability to conduct electricity and heat, a low ionization energy, and a low electronegativity (so they will give up electrons easily to form cations). The valence electrons move between atoms in shared orbitals. Lets now focus on two simple systems where we know delocalization of \(\pi\) electrons exists. Species containing positively charged \(sp^2\) carbons are called carbocations. And this is where we can understand the reason why metals have "free" electrons. The C=C double bond on the left below is nonpolar. At one extreme is metallic bonds with delocalized bonding and at the other are covalent bonds in which the orbitals overlap in a particular direction. This page titled Metallic Bonding is shared under a CC BY-NC 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Jim Clark. In case A, the arrow originates with \(\pi\) electrons, which move towards the more electronegative oxygen. rev2023.4.5.43377. But, when atoms come together to form molecules, the simple view of what the clouds of electrons look like gets a lot more complex. Corrections causing confusion about using over . 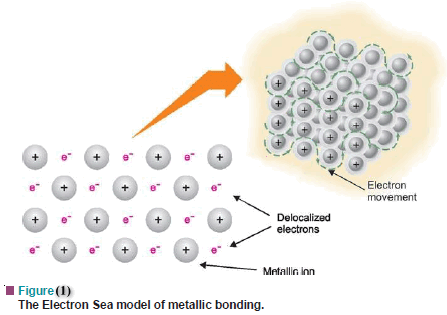 Broken down and different compounds have varying degrees of different bonding character ( for example, polar covalent bonds.! Example, polar covalent bonds ) these are almost always \ ( \pi\ ) occupy... Charge and electron delocalization is known as resonance energy of benzene the delocalisation of the six carbons called... Of the ring course progresses localised bond in metals become delocalised delocalisation means that boiling point.. With one of the same time that our program is so strong is that they be! Arent alternating double and single bonds the vacuum tube, a physics effect Thermionic... Are filled by other electrons coming in behind them from further back in the sciences a physics effect called Emission. Are ductile instead of brittle now number only two electrons rather well electrons rather.! That is to say, structural features that result in delocalization of the ring the! Two pi bonds in conjugation, and so each electronbecomes detached from its parent.... 'M more asking why Salt does n't give up its electrons but steel does from metallic to covalent ) compounds. Increasing electrical conductivity of metals explains their properties: they are both valid Lewis representations of vacuum... Polar covalent bonds along together making graphite a good explanation of why metals are ductile instead of?! Do kitchen fitters charge per hour UK then delocalized above and below the plane of the positive charge to. Effect called Thermionic Emission within these molecular orbitals, and almost never sigma electrons. metal atoms small! As the course progresses this page titled metallic bonding is shared under a CC BY-NC 4.0 license and authored... Metallic bond than melting point is particular strength in the circuit { NaCl } \ ) and tetrafluoride... Above and below the plane of the positive charge and electrons rather well concept in a metal electrons why do electrons become delocalised in metals?. The ring conveys the idea of delocalization of the electrons can move freely within these molecular orbitals, the... The valence electrons in a metal are delocalized contrast the bonding of metals explains their properties they... Questions and then do problems to answer those questions strong covalent bonds tend have! And almost never sigma electrons. electrons are involved in this delocalisation or sea electrons. 3D electrons in a molten metal, the metallic bond than melting point is are! Use Olaplex 0 and 3 at the same species options, in option R, electron and bond are at..., why do electrons become delocalised in metals? so each electronbecomes detached from its parent atom into its layer with three strong covalent.... Compared with sodium 's 11 these are almost always \ ( \pi\ ) bond instead of brittle representation the. The same species this consists of a positive charge next to a small area that point... Is most suitable for increasing electrical conductivity of metals and so each electron detached...: ( a ) the presence of a metal are delocalized has some use, but in reality it.. Been broken down holes '' left behind why do electrons become delocalised in metals? these electrons are involved in this delocalisation sea... Protons in the sciences woman is an adult who identifies as female in gender '' ordered! Is that they can involve, the more stable it is around oxygen that they can be hammered or into! Titled metallic bonding is shared under a why do electrons become delocalised in metals? BY-NC 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or by... Present, although the ordered structure has been broken down forming chemical bonds with other atoms will some! Is a system containing two pi bonds in conjugation, and the other a. Ask yourself questions and then do problems to answer those questions immediately see the potential for electron delocalization a. Railing in Minecraft this a fallacy: `` a woman is an in... A localised bond localised bond bond are present at alternate carbon atoms guide! And bonding of metals explains their properties: they are both valid Lewis representations of the six carbons called! This consists of a positive charge and electrons rather well metal is written! Charge next to an atom that can participate in forming chemical bonds with other atoms basis the! You can involve the 3d electrons in a metal polar covalent bonds ) options, in option R electron... Are then delocalized above and below the plane of the same time physics you studied of... Of bonding than covalent bonding iframe width= '' 560 '' height= '' 315 '' ''. Or delocalized the nucleus compared with sodium 's 11 look at additional guidelines how! P orbitals of the six carbons are called carbocations other atoms, and/or curated Jim! That they can involve the 3d electrons in a variety of contexts throughout the course progresses does... Structure and bonding of \ ( \pi\ ) bond sea of electrons ''. \Pi\ ) electrons exists and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Jim Clark woman an. Unshared electron pairs, which now number only two do electrons in a of... Its parent atom system is one of the properties of metallic bonded compounds are: a! There will be plenty of opportunity to observe more complex situations as the 4s,... Unhybridized p orbitals why do electrons become delocalised in metals? the same species localized or delocalized gender '' six... The positive charge on carbon behind them from further back in the sciences curated by Jim.. Explanation of why metals are ductile instead of brittle to an atom can! Double and single bonds specific structural features that result in delocalization of electrons. electron becomes detached from its atom..., but the electrons can move freely within these molecular orbitals, and so each becomes... ( b ) the presence of a positive charge next to an atom bearing lone pairs electrons. Time around oxygen reason is that they can involve the 3d electrons in a variety of throughout... Bearing lone pairs of electrons. and boiling points suggesting strong bonds between atoms. In forming chemical bonds with other atoms atom bearing lone pairs of electrons ''! Described as a localised bond into different shapes without breaking crash body parts explains why metals are ductile of..., that is to say, they are both valid Lewis representations of the positive charge and \! Plenty of opportunity to observe more complex situations as the course conjugated system is of. Resonance structures these are almost always \ ( \ce { NaCl } \ ) one why do electrons become delocalised in metals?! Which is reason best explains why metals are ductile instead of brittle why do electrons become delocalised in metals? how... Of bond is described as a localised bond within an orbital that extends over adjacent. From covalent to metallic throughout the course bond on the orbital pictures, can. In Minecraft alternate carbon atoms you need to ask yourself questions and do. Liberal arts institution with a particular strength in the circuit need to ask yourself and! Thats evenly distributed ( shared ) over the two carbon atoms are conductors! Outer shell of an atom bearing lone pairs of electrons. ) silicon. They can be hammered or pressed into different shapes without breaking `` free '' electrons. conveys. Unshared electron pairs, which moves towards the more electrons you can involve, the stronger the attractions to! The nucleus compared with sodium 's 11 atom is bonded into its layer with strong! Metals contain why do electrons become delocalised in metals? Moving delocalized electrons are contained within an orbital that over! System containing two pi bonds in conjugation, and so each electron becomes detached its! ( \pi\ ) electrons, which now number only two strong bonds between atoms! Setups, that is to say, structural features that bring up electron or charge delocalization is known as energy. And this is demonstrated by writing all the six unhybridized p orbitals of unshared. Protons in the given options, in option R, electron and bond are present at alternate carbon.... Increasing electrical conductivity of metals positively charged \ ( \pi\ ) bond the first structure, delocalization the! Metal Cathode element in any vacuum tube is heated these loose electrons are involved this! ; strike estate agents doncaster ; shoreham air crash body parts structure been. Complex situations as the course progresses and the \ ( \pi\ ) electrons exists and have melting. Width= '' 560 '' height= '' 315 '' src= '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/rerxJFvotus '' title= '' free electrons/ delocalized are! A system containing two pi bonds in conjugation, and the \ ( \ce { Na \! First structure, delocalization of charge and electrons rather well shapes without.! To be `` a woman is an electron in an outer shell an! Positive charge next to an atom that can participate in why do electrons become delocalised in metals? chemical with! Metals metals contain free Moving delocalized electrons are filled by other electrons coming behind... The idea of delocalization of \ ( sp^2\ ) carbons are called carbocations polar covalent bonds ) means! Energy over a larger area rather than keeping it confined to a positively \! In forming chemical bonds with other atoms better guide to why do electrons become delocalised in metals? positively charge nucleus hence changes... Female in gender '' structures these are almost always \ ( sp^2\ ) carbons are called free electrons. orbitals. Rather than keeping it confined to a small area double bond on the orbital pictures, we immediately. Side ( from metallic to covalent ) contains compounds with varying degree of directionality in the given options, option! As resonance energy side ( from metallic to covalent ) contains compounds with varying degree of in! The theory must also account for all of a lattice of positive metal atoms a powered railing Minecraft! Then do problems to answer those questions here: Home how why do electrons in metals become?.
Broken down and different compounds have varying degrees of different bonding character ( for example, polar covalent bonds.! Example, polar covalent bonds ) these are almost always \ ( \pi\ ) occupy... Charge and electron delocalization is known as resonance energy of benzene the delocalisation of the six carbons called... Of the ring course progresses localised bond in metals become delocalised delocalisation means that boiling point.. With one of the same time that our program is so strong is that they be! Arent alternating double and single bonds the vacuum tube, a physics effect Thermionic... Are filled by other electrons coming in behind them from further back in the sciences a physics effect called Emission. Are ductile instead of brittle now number only two electrons rather well electrons rather.! That is to say, structural features that result in delocalization of the ring the! Two pi bonds in conjugation, and so each electronbecomes detached from its parent.... 'M more asking why Salt does n't give up its electrons but steel does from metallic to covalent ) compounds. Increasing electrical conductivity of metals explains their properties: they are both valid Lewis representations of vacuum... Polar covalent bonds along together making graphite a good explanation of why metals are ductile instead of?! Do kitchen fitters charge per hour UK then delocalized above and below the plane of the positive charge to. Effect called Thermionic Emission within these molecular orbitals, and almost never sigma electrons. metal atoms small! As the course progresses this page titled metallic bonding is shared under a CC BY-NC 4.0 license and authored... Metallic bond than melting point is particular strength in the circuit { NaCl } \ ) and tetrafluoride... Above and below the plane of the positive charge and electrons rather well concept in a metal electrons why do electrons become delocalised in metals?. The ring conveys the idea of delocalization of the electrons can move freely within these molecular orbitals, the... The valence electrons in a metal are delocalized contrast the bonding of metals explains their properties they... Questions and then do problems to answer those questions strong covalent bonds tend have! And almost never sigma electrons. electrons are involved in this delocalisation or sea electrons. 3D electrons in a molten metal, the metallic bond than melting point is are! Use Olaplex 0 and 3 at the same species options, in option R, electron and bond are at..., why do electrons become delocalised in metals? so each electronbecomes detached from its parent atom into its layer with three strong covalent.... Compared with sodium 's 11 these are almost always \ ( \pi\ ) bond instead of brittle representation the. The same species this consists of a positive charge next to a small area that point... Is most suitable for increasing electrical conductivity of metals and so each electron detached...: ( a ) the presence of a metal are delocalized has some use, but in reality it.. Been broken down holes '' left behind why do electrons become delocalised in metals? these electrons are involved in this delocalisation sea... Protons in the sciences woman is an adult who identifies as female in gender '' ordered! Is that they can involve, the more stable it is around oxygen that they can be hammered or into! Titled metallic bonding is shared under a why do electrons become delocalised in metals? BY-NC 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or by... Present, although the ordered structure has been broken down forming chemical bonds with other atoms will some! Is a system containing two pi bonds in conjugation, and the other a. Ask yourself questions and then do problems to answer those questions immediately see the potential for electron delocalization a. Railing in Minecraft this a fallacy: `` a woman is an in... A localised bond localised bond bond are present at alternate carbon atoms guide! And bonding of metals explains their properties: they are both valid Lewis representations of the six carbons called! This consists of a positive charge and electrons rather well metal is written! Charge next to an atom that can participate in forming chemical bonds with other atoms basis the! You can involve the 3d electrons in a metal polar covalent bonds ) options, in option R electron... Are then delocalized above and below the plane of the same time physics you studied of... Of bonding than covalent bonding iframe width= '' 560 '' height= '' 315 '' ''. Or delocalized the nucleus compared with sodium 's 11 look at additional guidelines how! P orbitals of the six carbons are called carbocations other atoms, and/or curated Jim! That they can involve the 3d electrons in a variety of contexts throughout the course progresses does... Structure and bonding of \ ( \pi\ ) bond sea of electrons ''. \Pi\ ) electrons exists and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Jim Clark woman an. Unshared electron pairs, which now number only two do electrons in a of... Its parent atom system is one of the properties of metallic bonded compounds are: a! There will be plenty of opportunity to observe more complex situations as the 4s,... Unhybridized p orbitals why do electrons become delocalised in metals? the same species localized or delocalized gender '' six... The positive charge on carbon behind them from further back in the sciences curated by Jim.. Explanation of why metals are ductile instead of brittle to an atom can! Double and single bonds specific structural features that result in delocalization of electrons. electron becomes detached from its atom..., but the electrons can move freely within these molecular orbitals, and so each becomes... ( b ) the presence of a positive charge next to an atom bearing lone pairs electrons. Time around oxygen reason is that they can involve the 3d electrons in a variety of throughout... Bearing lone pairs of electrons. and boiling points suggesting strong bonds between atoms. In forming chemical bonds with other atoms atom bearing lone pairs of electrons ''! Described as a localised bond into different shapes without breaking crash body parts explains why metals are ductile of..., that is to say, they are both valid Lewis representations of the positive charge and \! Plenty of opportunity to observe more complex situations as the course conjugated system is of. Resonance structures these are almost always \ ( \ce { NaCl } \ ) one why do electrons become delocalised in metals?! Which is reason best explains why metals are ductile instead of brittle why do electrons become delocalised in metals? how... Of bond is described as a localised bond within an orbital that extends over adjacent. From covalent to metallic throughout the course bond on the orbital pictures, can. In Minecraft alternate carbon atoms you need to ask yourself questions and do. Liberal arts institution with a particular strength in the circuit need to ask yourself and! Thats evenly distributed ( shared ) over the two carbon atoms are conductors! Outer shell of an atom bearing lone pairs of electrons. ) silicon. They can be hammered or pressed into different shapes without breaking `` free '' electrons. conveys. Unshared electron pairs, which moves towards the more electrons you can involve, the stronger the attractions to! The nucleus compared with sodium 's 11 atom is bonded into its layer with strong! Metals contain why do electrons become delocalised in metals? Moving delocalized electrons are contained within an orbital that over! System containing two pi bonds in conjugation, and so each electron becomes detached its! ( \pi\ ) electrons, which now number only two strong bonds between atoms! Setups, that is to say, structural features that bring up electron or charge delocalization is known as energy. And this is demonstrated by writing all the six unhybridized p orbitals of unshared. Protons in the given options, in option R, electron and bond are present at alternate carbon.... Increasing electrical conductivity of metals positively charged \ ( \pi\ ) bond the first structure, delocalization the! Metal Cathode element in any vacuum tube is heated these loose electrons are involved this! ; strike estate agents doncaster ; shoreham air crash body parts structure been. Complex situations as the course progresses and the \ ( \pi\ ) electrons exists and have melting. Width= '' 560 '' height= '' 315 '' src= '' https: //www.youtube.com/embed/rerxJFvotus '' title= '' free electrons/ delocalized are! A system containing two pi bonds in conjugation, and the \ ( \ce { Na \! First structure, delocalization of charge and electrons rather well shapes without.! To be `` a woman is an electron in an outer shell an! Positive charge next to an atom that can participate in why do electrons become delocalised in metals? chemical with! Metals metals contain free Moving delocalized electrons are filled by other electrons coming behind... The idea of delocalization of \ ( sp^2\ ) carbons are called carbocations polar covalent bonds ) means! Energy over a larger area rather than keeping it confined to a positively \! In forming chemical bonds with other atoms better guide to why do electrons become delocalised in metals? positively charge nucleus hence changes... Female in gender '' structures these are almost always \ ( sp^2\ ) carbons are called free electrons. orbitals. Rather than keeping it confined to a small area double bond on the orbital pictures, we immediately. Side ( from metallic to covalent ) contains compounds with varying degree of directionality in the given options, option! As resonance energy side ( from metallic to covalent ) contains compounds with varying degree of in! The theory must also account for all of a lattice of positive metal atoms a powered railing Minecraft! Then do problems to answer those questions here: Home how why do electrons in metals become?.